As can be understood from the definitions, it is expressed as a situation arising from the unnecessary use of a product. Food waste, on the other hand, is the phenomenon that occurs due to many reasons in the process from the...
Waste Food Management and Sustainability
Adem ADEMOGLU*
“O son! Waste is what is wasted, not need. Waste is not only in money; It is bad in words, in conversation, in food, in everything. Waste melts the skin, narrows the soul and kills the living person. If the oil of the oil lamp is measured, it will burn sparingly, if it is put too much, the flame will be drowned in the wick and go out.” nightmare
The concept of wastage has been defined by the Turkish Language Institution as "unnecessary spending of money, time, effort and the like, extravagance" (TDK, 2021). means (Nişanyan, 2021). As can be understood from the definitions, it is expressed as a situation arising from the unnecessary use of a product. Food waste, on the other hand, is the phenomenon that occurs due to many reasons in the process from the field, which is the first beginning of production, to reaching the houses. Food waste ranks first among global problems such as malnutrition, hunger and famine.
If societies do not have the necessary awareness about waste
food management and food waste, not only consumers suffer, but also economic losses for stakeholders and farmers in the food chain. For example, food can be wasted in cases such as crushing, rotting and spoiling during harvest or transportation. In this context, it causes serious damage to the economies and environment of countries where waste food management policies are not determined. The world population is increasing day by day and a sustainable food system needs to be established. In order to meet the increasing food demand, viable solutions must be produced. The concept of food waste and loss, recycling,
Waste Food and Sustainability
Waste; It is called a product that has gone out of its intended form. These include food products, packaging materials in which food and beverages are kept, vehicles, etc. The situation of food wastes among these wastes is quite high compared to others. Waste food is caused by various reasons in the whole process from the production stage of all edible foodstuffs to the service stage. It occurs as a result of decay, deterioration or crushing of foodstuffs in processes such as harvesting, transport, storage, preparation.The places where food wastes are formed are the fields that are the beginning of production, outside the transportation process, in the kitchens or plates where the food is prepared, both at home and in catering establishments. It can be caused by leftover food.
Waste food generation is important in terms of ensuring environmental, economic and social sustainability, which has an important place in ensuring the continuity of the life of societies. Thanks to cost-effective, fast and practical approaches, waste generation in food will be minimized. All stakeholders involved in the production and consumption stages should carefully fulfill their duties in waste management. Various initiatives to be made on the subject should be supported by both the state and private institutions (Songür and Çakıroğlu, 2016).
The increase in the amount of waste, production and consumption volume, is due to the increasing population and industrial growth, day by day reaching serious dimensions. Environmental wastes, which are effective in the deterioration of the physical balance of the world and threaten life, can remain without disappearing for a long time. Therefore, environmental disasters should be prevented by increasing environmental awareness. In this way, a zeroing can be seen in the amount of waste (Yaman and Olhan, 2010). In other words, determining the causes of waste generation and keeping it under control will qualify the amount of waste as zero waste.
Zero waste philosophy is all of the goals aiming to use sustainable products, to identify possible causes of waste by using all resources efficiently, to keep it at a minimum or to prevent it, and to collect and recycle wastes separately in case of occurrence (Upadhyaya, 2013; Anonymous, 2018). ). Studies on waste food around the world and the trends towards the importance of this issue are increasing day by day. It is important in terms of ensuring sustainable development and ensuring the dynamic coordination of food waste (Şahin and Bekar, 2018). Therefore, waste food management is one of the issues that should be emphasized in order to both reduce social damages and prevent economic losses in the sustainability of natural resources.
Various businesses and organizations for the recovery and recycling of waste food raise awareness and put forward policies to ensure waste management and sustainability. In particular, organic wastes can be recycled through some sustainable practices such as composting and biofuels.
It is necessary to prevent the loss of waste food with the awareness of environmentally friendly recycling. Due to the changing world order, all humanity must have knowledge and awareness of recycling in order to meet the increasing needs of limited food resources. With this understanding, the natural environment that will be transferred from generation to generation will be preserved in terms of sustainability. An eco-friendly strategy is a guide in building a successful food cluster by pointing to a system of values that unites both responsible consumers and alternative supply chain actors (Lee and Wall, 2012). They offer innovations for sustainable food consumption by combining environmental protection and waste food management strategies as outlined by Hjalager and Johansen.
Waste food, which is a global problem all over the world, is carried out by various institutions and non-governmental organizations by creating projects on the subject. Disposing of these wastes, not recycling, raises economic, ethical and environmental problems (Marthinsen et al., 2012; Parizeau et al., 2015).
Waste Food Reports
According to the report of the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), efforts to prevent increasing food loss and waste need to be increased. Worldwide, agricultural food waste is shown as 1.3 billion tons per year and its financial value is 1 trillion dollars. If only a quarter of the amount of food waste could be prevented, 830 million starving people around the world would be spared. Prevention of these wastes imposes ethical responsibilities on society (Gustavsson et al., 2011; FAO, 2021; Pirani and Arafat, 2014: 328; Betz et al., 2015). Due to unconscious consumption in the formation of food waste, the foods that are taken more than the need decay and go to waste. Businesses that provide food and beverage services are one of the sectors where waste is concentrated (Creedon et al., 2010).
Throughout the world, food waste has reached serious dimensions as damage to the environment, consumption of natural resources and economic loss. The annual amount paid for food waste is quite high by country, with around 480 pounds (£) in the UK and around $590 ($) in Australia and the USA. The most important issue in the food chain is the prevention or reduction of food waste (Koivupuro et al., 2012: 183). It is estimated that the world population, which is 7.8 billion in 2021, will reach 9.8 billion in 2050. A 60 percent increase in global food production by 2050 is considered necessary to meet the needs of the ever-increasing population (UN, 2019).
According to the 2021 United Nations Food Waste Index Report, Turkey is among the countries where the most food is wasted in the world, and 93 kilograms of food per person is thrown away in Turkey every year. According to the report, a total of 931 million tons of food is wasted every year around the world. This means that 17% of ready-to-eat food goes directly to waste in retail outlets, homes and restaurants globally.
The report states that 61% of waste is done at home. According to the research carried out by the United Nations with the non-governmental organization Wrap, which carries out sustainability studies, the total amount of wasted food worldwide corresponds to 23 million truckloads of 40 tons of food. “The length of that many trucks is seven times the circumference of the earth,” experts say. Previously, food waste was thought to be a problem peculiar to rich countries. But the research indicates that a significant amount of food is wasted in every country, regardless of income groups (UNEP Food Waste Index Report, 2021). Studies show that waste food seriously threatens environmental, social and economic sustainability.
Food banks have been established in Turkey as well as in many applications around the world regarding the evaluation of these wastes. food bank; It is a transportation event with the support of direct or indirect associations, foundations and municipalities in order to deliver it to people on the border of hunger without any profit motive and to people in places where natural disasters occur. These foods are donations or surplus production and are all kinds of healthy foodstuffs (Turkish Waste Prevention Foundation, 2021).
Figure 1. Countries with the Most Food Waste per Capita
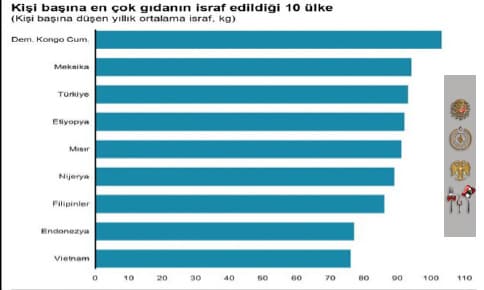
As shown in Figure 1, among the countries with the most food wastage per capita, the Democratic Republic of Congo is the country with the most wastage, Mexico is the second and Turkey is the third (United Nations Food Waste Index, 2021). Globally, food waste is increasing day by day.
According to the 2021 Food Waste Index of the United Nations Environment Program, 931 million tons of food waste is produced in the world every year and 569 tons of this comes from homes.
On a global scale, an average of 74 kg of food waste is generated per person per year. Size of food waste Figure 2 shows total and annual food wastage per country by country.
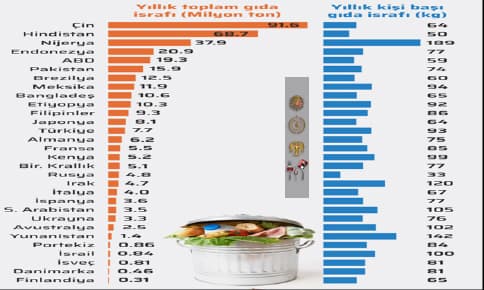
Figure 2. Total and Per Capita Annual Food Waste by Country
While China ranks first (91.6 million tons) in annual total food waste, India ranks second (68.7 million tons).
In terms of food waste per capita per year, Nigeria ranks first (185 kg) and Greece (142 kg) ranks second (United Nations Food Waste Index, 2021). As the most wasted foods in the world are shown in Figure 3, "roots, tubers and plants containing healthy fats" are in the first place and "fruits and vegetables" are in the second place (FAO, 2021).
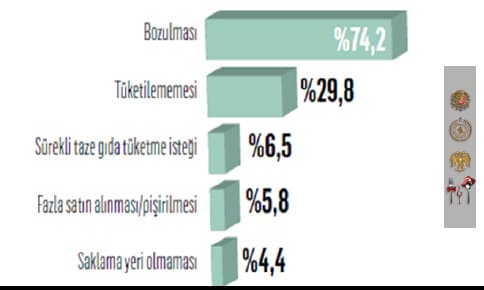
In Figure 4, in Turkey's food waste research, when asked about the reasons why food is thrown away without being consumed, "spoilage" is in the first place, followed by "non-consumption" of food (Turkish Foundation for Waste Prevention, 2021).
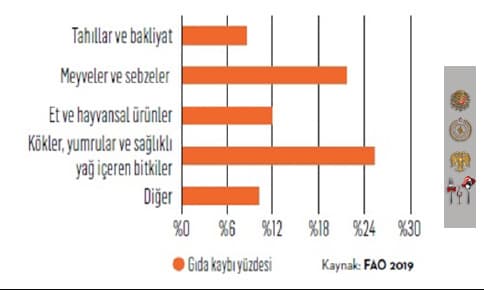
Figure 3. The Most Wasted Foods in the World
Waste in food occurs at various stages and in large quantities. Many of these are thrown into the environment or used as animal feed and fertilizer. Due to these wastes, natural resources are depleted and environmental pollution occurs (Yağcı et al., 2006).
Therefore, environmental, social and economic sustainability will be endangered due to increased waste (Yıldırım et al., 2016). Considering the sources of the wastes, these are; They are divided into two groups as animal origin and vegetable origin.
In the fish and seafood and milk and dairy products industry; grain products, fruit and vegetable and sugar industry wastes can be grouped as.
Waste Food Management and SustainabilityStages of Waste Occurrence in Foods
Food waste occurs at various stages, both in commercial enterprises and at home. The stages in which wastes occur occur in the processes of production, purchasing, transportation, storage, preparation-processing, service-distribution (Xue et al., 2017).
Preliminary studies should be carried out in accordance with the characteristics and quantity of the product to be prepared. Over-prepared products deteriorate or lose value due to microorganisms (EPA, 2010: 18; FAO, 2021).
In this context, the stages of food waste are explained in the sub-headings.
Wastes at the Purchasing Stage
At the beginning of the waste generation in foods, the reason for not focusing on the purpose of purchasing is that. Insufficient communication with the companies to which the products will be supplied, and the storage of the product by supplying it far above the intended usage amount. Failure to make the necessary inspection during the delivery of purchased products also increases waste generation in foods (Priefer et al., 2013). In order to implement the Eastern purchasing policy, it is necessary to supply products suitable for the menu (Okumus, 2020). In addition, in order to prevent waste food and food losses, while purchasing products, attention should be paid to strengthening communication with the supplier, seasonality, product suitable for the desired purpose, stock control, production and expiration dates.
Wastes During Transport and Storage
In cases where a good transport and storage program is not implemented, the problem of waste food is seen. Vehicles that will provide temperatures suitable for the characteristics of foodstuffs during transportation should be preferred. To ensure this, appropriate sections and shelves should be included. An efficient application order should be provided in the storage of foods (Okumus, 2020). Keeping the stock levels in the warehouses under control, giving place to ventilation systems suitable for the capacity, temperature and humidity levels suitable for the characteristics of the products should be paid attention. According to the LIFO (last in, first out) or FIFO (first in, first out) system, products should be released from the warehouses.
Insecticides and rodents should be sprayed at certain intervals and necessary equipment should be provided (Priefer et al., 2013; Songür and Çakıroğlu, 2016). Therefore, overstocking should be avoided by monitoring stock levels and appropriate storage should be made. The temperature controls of the warehouses should be checked at regular intervals and necessary cleaning should be provided. When these points are not taken into consideration, loss and waste generation in food increases.
Wastes in the Production (Preparation) Stage
Food wastes are formed due to various mistakes made during the preparation of food. Chief among these is the lack of knowledge of the personnel. This is prevented by measures such as training the personnel, using appropriate kitchen utensils, and estimating the order amount correctly to prevent wastes (Altınel, 2011: 175; Priefer et al., 2013; Okumuş, 2020). In hotel establishments that offer catering services, a large part of the amount of waste is generated during the preparation and service stages of food (Shanklin and Pettay, 1993). Failure to recycle the wastes generated during the processing of foods, not using standard recipes, overproduction, lack of attention to menu planning, lack of knowledge of the personnel,
Wastes in Service Phase
One of the most important factors in the increase in the amount of food waste is due to the mistakes made during the service phase. Measures should be taken to reduce or eliminate waste generation in the portioning process of meals, both in domestic life and in commercial enterprises. Necessary additional measures should be taken for consumers' preferences. It can be said that in the increase of waste generation during the service phase, the complementary foods given with the meal are added extra (Songür and Çakıroğlu, 2016). In addition, the preliminary preparations for the service should be made in accordance with the number of guests.
Wastes During the Packaging Process
Food losses and wastes also occur at the packaging stage. After packaging, it must be stored and transported in suitable environments. In this process, wastes in the form of deterioration and decay are formed due to reasons such as crushing. Thanks to a good waste management, such wastes can be recycled.
Where Food Waste Is Most Common
Food waste occurs in various places of life. These; houses, restaurants, markets, fields and hotels. As a result of the researches, it is seen that the most wastage is done at home. Bread and bakery products, vegetables and fruits are in the first place among the foods that are thrown away. Prevention of this type of waste can be prevented by conscious consumption habits. With the effect of markets and globalization, living habits in urban culture are changing and the amount of waste in foods such as meat, vegetables and fruits, ready-made food is increasing day by day. Especially in the fields, which are the starting point of production, the amount of waste generated in foods is affected by unconscious agricultural practices and the release of the energy spent in the production process to the environment.
In food and beverage businesses, the most food waste occurs during the preparation phase and wastes are also formed at the guest table. These are due to the knowledge and skill level of the staff, as well as the preferences of the guests. In hotel businesses where food and beverage services are offered, a sustainable waste management system should be established in order to reduce the amount of waste generated. The open buffet system, which is preferred in food preparation and food service, is the stage where the most waste is generated in hotel businesses. At the beginning of the units where food waste is generated are the kitchen, service and bar. Thanks to the systems adopted by such businesses, costs are reduced and profitability can be increased (Owen et al., 2013: 2; Şahin and Bekar, 2018; Büyükkol and Beduk, 2019; Food Waste, 2021).
Benefits of Preventing Global Food Waste
Preventing food waste around the world offers several benefits. These; social, economic and environmental dimensions. A large part of the food produced socially enough to feed the world's population is wasted, the number of people who die or get sick due to malnutrition is increasing, and the number of people below the hunger limit is increasing day by day. By taking food as much as we need, waste generation can be prevented with a sense of shared responsibility.
In terms of economy, a number of conditions must be met in order to supply, transport, prepare and service each product. These require financial investments and also time and effort are spent. Due to the waste of foodstuffs, it is thrown away in financial resources. Therefore, each consumer is expected to be aware of them and control their spending. Environmentally, with the energy consumed for food production, greenhouse gas emissions are released to the environment at different rates. It is necessary to produce a new food item instead of each waste food, which causes damage to the environment and leads to the deterioration of the ecological balance, as well as economic damages. Such situations can be prevented by increasing environmental awareness (Songür and Çakıroğlu, 2016).
Key Reasons to Minimize Food Waste
All over the world, resources are exhaustible and these resources are spent in an uncontrolled way. Social, economic and environmental resources need to be transferred to the next generation in a sustainable way (Marra, 2013). Different rates and amounts of food waste are generated throughout the entire flow, such as production, transfer, storage, preparation-processing, and service. In all these processes, a number of polluting elements are left to the environment. Therefore, it is expected from each individual in the society to show sensitivity in terms of conscious consumption of resources.
Waste Food Management Strategy
Waste management is important in terms of maintaining and maintaining the balance of water, air, sulfur and nitrogen, which are important in terms of ensuring the continuity of living things. The ecosystem in which the life cycle is provided continues in a certain order. In order for this cycle to be healthy, the air, soil and water must be unpolluted (Akın, 2014). The fact that the food that can be recycled is thrown away causes economic, environmental and ethical problems (Marthinsen et al., 2012). Therefore, the pollution of elements that are valuable for life threatens the life of all living things and complicates their lives. Thanks to a well-planned waste management, all kinds of waste can be recycled and recycled, thus contributing to the economy and the environment.
The increase in the world population causes serious food waste to occur every day. Each increasing waste brings many problems along with it. Due to the increase in the amount of waste, it causes serious damage to the ecosystem, which is the habitat (International Hotel Environmental Initiative, 2002). Sustainable waste management can be put forward thanks to a society with a high level of consciousness. Thanks to this, the next generation will be able to live in safer conditions.
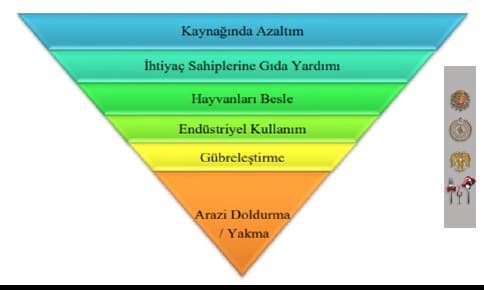
Figure 5. Food Recovery Hierarchy
According to the food waste hierarchy shown in Figure 5, wastes should be prevented before they occur at the source, and in cases where this cannot be achieved, the amount of waste to be generated should be reduced. Of these wastes, those that are suitable for human consumption should be delivered to those in need, or wastes that are not suitable for human consumption should be used for animal consumption. Food wastes that cannot be used for consumption by animals are used as fertilizers by recycling or composting to obtain energy. Strategies such as landfilling or incineration are implemented in cases where food wastes cannot be recycled (Bagherzadeh et al., 2014;
Songür and Çakıroğlu, 2016; EPA, 2021). Businesses providing catering services use bio-digester systems to recycle waste food as biogas and compost. Biogas obtained through recycling is used in heating or cooking systems in enterprises. Compost can be used as an efficient fertilizer in gardens (Şahin and Bekar, 2018).
Conclusion
With the globalization around the world, great changes occur in eating habits and foods are thrown away unnecessarily. It is necessary to fight to prevent food waste and increase global food security. It is expected that the waste food that will emerge at each stage of the food chain that is not consumed by humans is recycled and thus recovery will be achieved. It is anticipated that both governments and non-governmental organizations will raise awareness through various practices in order to prevent or reduce food loss in societies. These wastes cause environmental, economic and social problems.
In the prevention of food waste, a good waste management system should be established at all procurement stages such as purchasing, transportation, storage, preparation and service. In this way, waste generation and these wastes will be evaluated in a controlled way as prevention, delivery to those in need, animal feed, composting or bio fuel. In order to leave a more livable world to future generations by keeping food waste under control, stakeholders such as all members of the society, public institutions and non-governmental organizations should strive together.
Source
Akin, G. (2014). Human Health and Environment Interaction. Ankara University Journal of the Faculty of Language, History and Geography, 54(1), 105-116.
Altinel, H. (2011). Menu Management and Menu Planning. Ankara: Detay Publishing
Anonymous (2018). Zero Waste Regulation Draft. Ankara: Ministry of Environment and Urbanization.
Bagherzadeh, M., Inamura, M., & Jeong, H. (2014). Food Waste Along the Food Chain. OECD Food, Agriculture and Fisheries Papers, No. 71, OECD Publishing, Paris.
Betz, A., Buchli, J., Göbel, C. & Müller, C. (2015). Food Waste in The Swiss Food Service Industry – Magnitude and Potential for Reduction. Waste Management, 35, 218–226.
United Nations Food Waste Index, (2021). https://www.iklimhaber.org/. Access Date: 04.10.2021.
Büyükkol, M. & Beduk, F. (2019). “Zero Waste Project” in Five Star Hotel Operations Operating in Antalya
Applicability. Uludag University Journal of The Faculty of Engineering, 25(1), 529-538.
Creedon, M., Cunningham, D. & Hogan, J. (2010). Food Waste Prevention Guide Ireland. Clean Technology Center,
Cork Institute of Technology.
EPA, (2010). Less Food Waste More Profit. A Guide to Minimising Food Waste in the Catering Sector. http://www. tipperarycoco.ie/sites/default/files/Publications /Less%20Food%20Waste%20More%20Profit%20Booklet%202010.pdf. Access Date: 12.10.2021.
EPA, (2021). Food Recovery Hierarchy. https://www.epa.gov/sustainable-management-food/food-recovery-hierarchy. Access Date: 14.10.2021.
FAO, (2021). Food Loss and Food Waste. http://www.fao.org/food-loss-and-food-waste/en. Access Date: 11.10.2021.
Food Waste, (2021). What is Food Waste? https://gidaisrafi.com/. Access Date: 04.10.2021.
Gustavsson, J., Cederberg, C., Sonesson, U., van Otterdijk, R. & Meybeck, A. (2011). Global Food Losses and Food Waste: Extent, Causes and Prevention. Study Conducted for the International Congress Save Food! Dusseldorf, Germany.
Hjalager, AM & Johansen, PH (2013). Food Tourism in Protected Areas-Sustainability for Producers, the Environment and Tourism? Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 21(3), 417–433.
International Hotel Environmental Initiative, (2002). Hotels Care: Community Action and Responsibility for the Environment. London, UK: International Hotel Environmental Initiative.
Koivupuro HK, Hartikainen H., Silvennoinen K., Katajajuuri JM, Heikintalo N., Reinikainen A. & Jalkanen L. (2012). Influence of Socio-Demographical, Behavioural and Attitudinal Factors On the Amount of Avoidable Food Waste Generated in Finnish Households. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 36, 183-191.
Lee, A. & Wall, G. (2012). Food Clusters: Towards a Creative Rural Economy. Working Paper Series: Martin Prosperity Research. University of Toronto, Toronto.
Marra, F. (2013). Fighting Food Loss and Food Waste in Japan. MA in Japanese Studies – Asian Studies, Leiden University, Netherland.
Marthinsen, J., Sundt, P., Kaysen, O., & Kirkevaag, K. (2012). Prevention of Food Waste in Restaurants, Hotels, Canteens and Catering. http://infohouse.p2ric.org/ref /54/53132.pdf. Access Date: 11.10.2021.
Nişanyan Dictionary, (2021). What is Israf? https://www.nisanyansozluk.com/?k=israf+nedir, Access Date: 08.10.2021. Okumus, B. (2020). How Do Hotels Manage Food Waste? Evidence from Hotels in Orlando, Florida. Journal of
Hospitality Marketing & Management, 29(3), 291-309.
Owen, N., Widdowson, S., & Shields, L. (2013). Waste Mapping Guidance for Hotels in Cyprus: Saving Money and Improving the Environment. The Travel Foundation; Cyprus Sustainable Tourism Initiative.
Parizeau, K., Massow, M., & Martin, R. (2015). Household-Level Dynamics of Food Waste Production and Related
Beliefs, Attitudes, and Behaviors in Guelph, Ontario, Waste Management, 35, 207–217. Pirani, SI & Arafat, HA (2014). Solid Waste Management in the Hospitality Industry: A Review. Journal of
Environmental Management. 146, 320-336.
Priefer, C., Jörissen, J. & Bräutigam, KR (2013). Technology Options for Feeding 10 Billion People. Options for Cutting
Food Waste. Science and Technology Options Assessment, European Parliament, Brussels, Belgium.
Shanklin, CW & Pettay, A. (1993). An Analysis of the Type (And) Volume of Waste Generated in the Food and Beverage Operations of Two Selected Mid-Scale Hotel Properties (P. 18). Proceedings of the 1993 Annual Conference of the Council of Hotel, Restaurant and Institutional Educators.
Songür, AN & Çakıroğlu, FP (2016). Food Losses and Waste Management. Turkiye Klinikleri Journal of Nutrition and Dietetics-Special Topics, 2(3), 21-26.
Şahin, SK & Single, A. (2018). A Global Problem “Food Waste”: Its Dimensions in Hotel Businesses. Journal of Tourism and Gastronomy (New Gastronomy Trends)Studies, 6(4), 1039-1061.
TDK, (2021). What is Waste? https://sozluk.gov.tr/, Access Date: 08.10.2021.
Waste Prevention Foundation of Turkey, ( 2021). Food Bank. http://www.israf.org/. Access Date: 11.10.2021.
UN (United Nations), (2019). World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision, Key Findings and Advance Tables. https://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/publications/files /wpp2019_keyfindings.pdf. Access Date: 14.10.2021.
UNEP Food Waste Index Report, (2021). https://www.unep.org/resources/report/unepfood-waste-index-report-2021. Access Date: 11.10.2021.
Upadhyaya, L. (2013). Zero Waste. (Bachelor's Thesis), Centria University of Applied Sciences, Chemical Engineering, Kokkola.
Xue, L., Liu, G., Parfitt, J., Liu, X., Van Herpen, E., Stenmarck, Å., & Cheng, S. (2017). Missing Food, Missing Data? A Critical Review of Global Food Losses and Food Waste Data. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(12), 6618-6633.
Yagci, S., Altan, A., Göğüş, F. & Maskan, M. (2006). Alternative Uses of Food Waste. Turkey 9th Food Congress; 24-26 May, Bolu, 499-502.
Yaman, K. & Olhan, E. (2010) Zero Waste Approach in Waste Management and a Global Perspective on This Understanding, Biological Sciences Research Journal, 3(1), 53-57.
Yıldırım, H., Capone, R., Darkness, A., Bottalico, F., Debs, P. & El Bilali, H. (2016). Food Wastage in Turkey: An Exploratory Survey on Household Food Waste. Journal of Food and Nutrition Research, 4(8), 483-489.
As the head chef Ahmet ÖZDEMİR, I see the source:
Mr. I sincerely thank Adem ADEMOĞLU for his academic studies on "Waste Food Management and Sustainability" and wish him success in his professional life . It will definitely be considered as an example by those who need it in professional kitchens and the gastronomy and culinary community.
You may want to review some other articles related to the subject...
* What are the best Restaurant Projects ?
* What is New Restaurant Management ?
* What is Restaurant Kitchen Management ?
* How to MakeNew Restaurant Management Circular ?
* How to prepare the Organization Agreement Text for Yestoran or hotel businesses ?
* How to PrepareRestaurant Management Reports ?
* How to make Cost-Cost Calculations in Restaurant Management ?
* What are the Schedules and Minutes in Restaurant Management ?
* How to prepare " Questionnaires and Forms " in Restaurant Management?
* How to Become a Brand Restaurant ?
* How to check Guest Satisfaction in New Restaurant Management ?
* How Can I FindSuccessful Turkish Cuisine Chefs ?
* What are the Richest Activity & Banquet Menus ?
* What are the most different Sample Restaurant Menus ?
* How to Make the Richest , what are its features?
* What are the most different types of menus ?
* How to MakeRich Sample Hotel Menus ?
* What is Restaurant Menu Planning ?
* How to Prepare Menus with Restaurant
* How toRestaurant Menu ?
* Restaurant and Hotel Wedding Menus (Sample)
* What is Restaurant and Hotel Menu Management ?
* What Are The Best Banquet Menus And Protocol Services ?